Cardboard tubes, cylindrical structures made of paperboard, play a crucial role in various industries due to their versatility and durability. These tubes find applications in packaging, construction, arts and crafts, and more. They provide a practical and eco-friendly solution for a wide range of needs. Read More…
Valk Industries provides engineering and manufacturing services for cardboard tubes as well as custom thermoformed items like clamshells, blister packs, trays and filler material.

Western Container partners with the world`s top spiral tube equipment designers & paperboard manufacturers, to bring our customers the very best paper tubing and precision cores.

Chicago Mailing Tube is a premier manufacturer of custom paper tubes, containers, and cores, providing products that are both high quality and economical.

Here at Paper Tubes and Sales we are a proven manufacturer of high quality cardboard tubes. These products are ideal for a multitude of industries and our teams are available to assist you with determining the best paper tube for your application.

Marshall Paper Tube Company designs and manufactures custom labeled cans, tubes, and mailings. We can create amazing custom designs in full color for your product or brand. We also provide specialty items like coin collection banks and fundraising cans. All of our products are made in the United States of America and out of 100% recycled paperboard in an effort to stay “green.”
More Cardboard Tube Manufacturers
What are the industrial uses of cardboard tubes?
Answer: Cardboard tubes, also known as paper tubes, fiber tubes, or cardboard cores, play a fundamental role across numerous industries because of their adaptability, durability, and cost-efficient manufacturing. Their value lies in their ability to be engineered in a wide range of sizes, wall thicknesses, and strengths, making them indispensable for multiple applications. Here’s a comprehensive look at the key industrial uses of cardboard tubes:
- Packaging and Shipping:
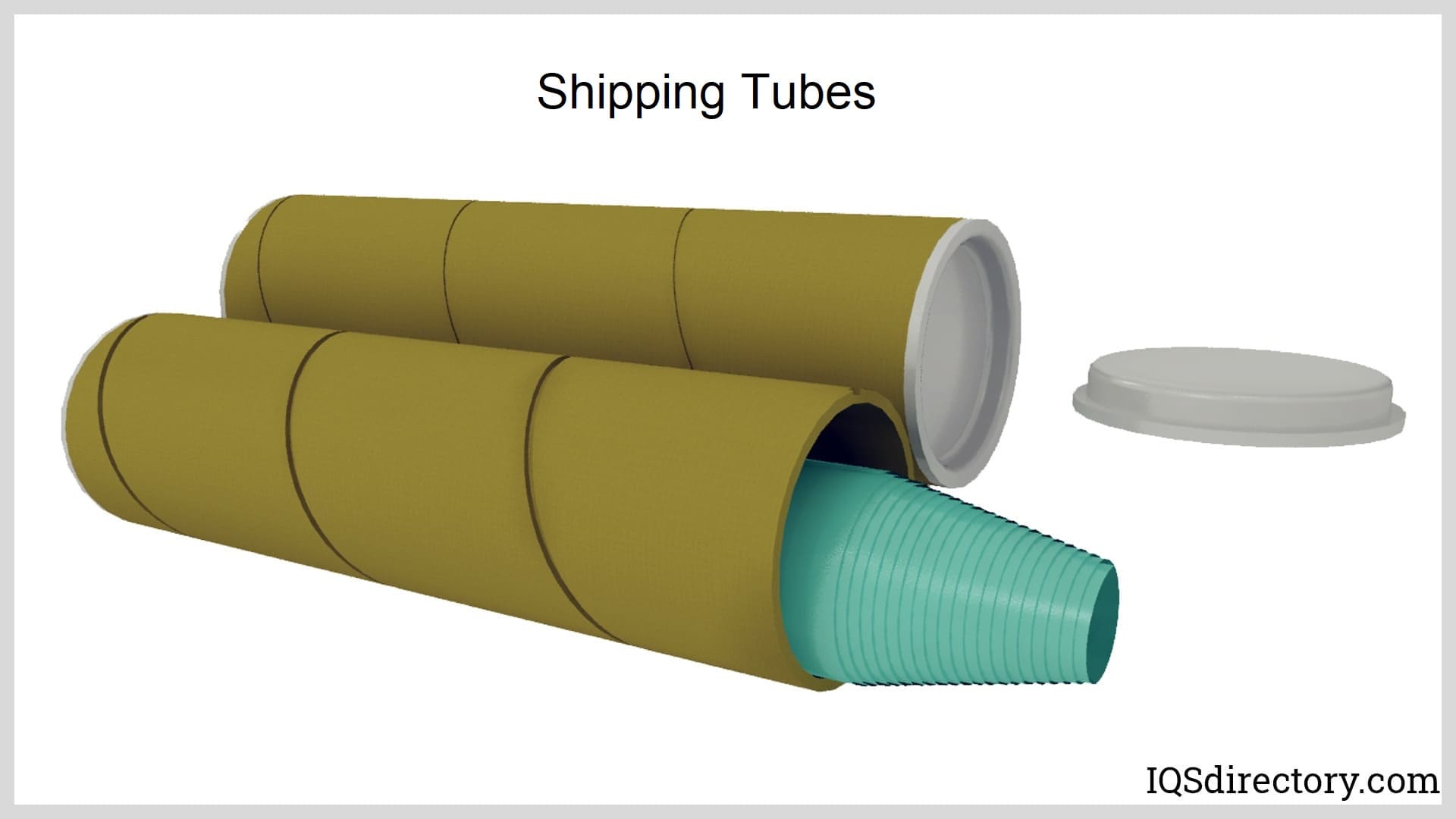
- Protective Sleeves: Cardboard tubes are relied upon to protect elongated or delicate items—such as posters, architectural blueprints, rods, or pipes—during transit. The rigid structure prevents crushing, bending, or creasing, ensuring items arrive in pristine condition.
- Mailing Tubes: These tubes are a staple for shipping rolled documents, artwork, certificates, or small parts. Their robust construction withstands the rigors of postal handling, while end caps provide additional security.
- Palletization: Heavy-duty tubes act as spacers or core supports on pallets, stabilizing bulk goods for safe stacking and storage in warehouses or distribution centers.
- Material Handling and Storage:
- Cores for Winding: Industries such as textiles, paper production, flexible packaging, plastic film, and metal foil use cardboard tubes as winding cores. These cores facilitate efficient material handling, storage, and transportation by keeping products tightly wound and protected.
- Spools and Bobbins: In sectors like wire, cable, yarn, and rope manufacturing, tubes serve as spools or bobbins, allowing for easy winding, unwinding, and dispensing during production or installation.
- Construction and Structural Applications:
- Concrete Formwork: Large-diameter cardboard tubes, such as Sonotubes, are used as molds for pouring concrete columns, pillars, and footings. Their lightweight, disposable nature reduces labor and cleanup costs on construction sites.
- Void Formers: Tubes form intentional cavities in concrete slabs or walls, reducing overall weight and facilitating passage for utilities like electrical conduits or plumbing.
- Manufacturing and Processing:
- Textile Industry: Cardboard tubes act as carriers for yarn and thread during weaving, spinning, and dyeing, supporting high-speed processing and minimizing tangling or breakage.
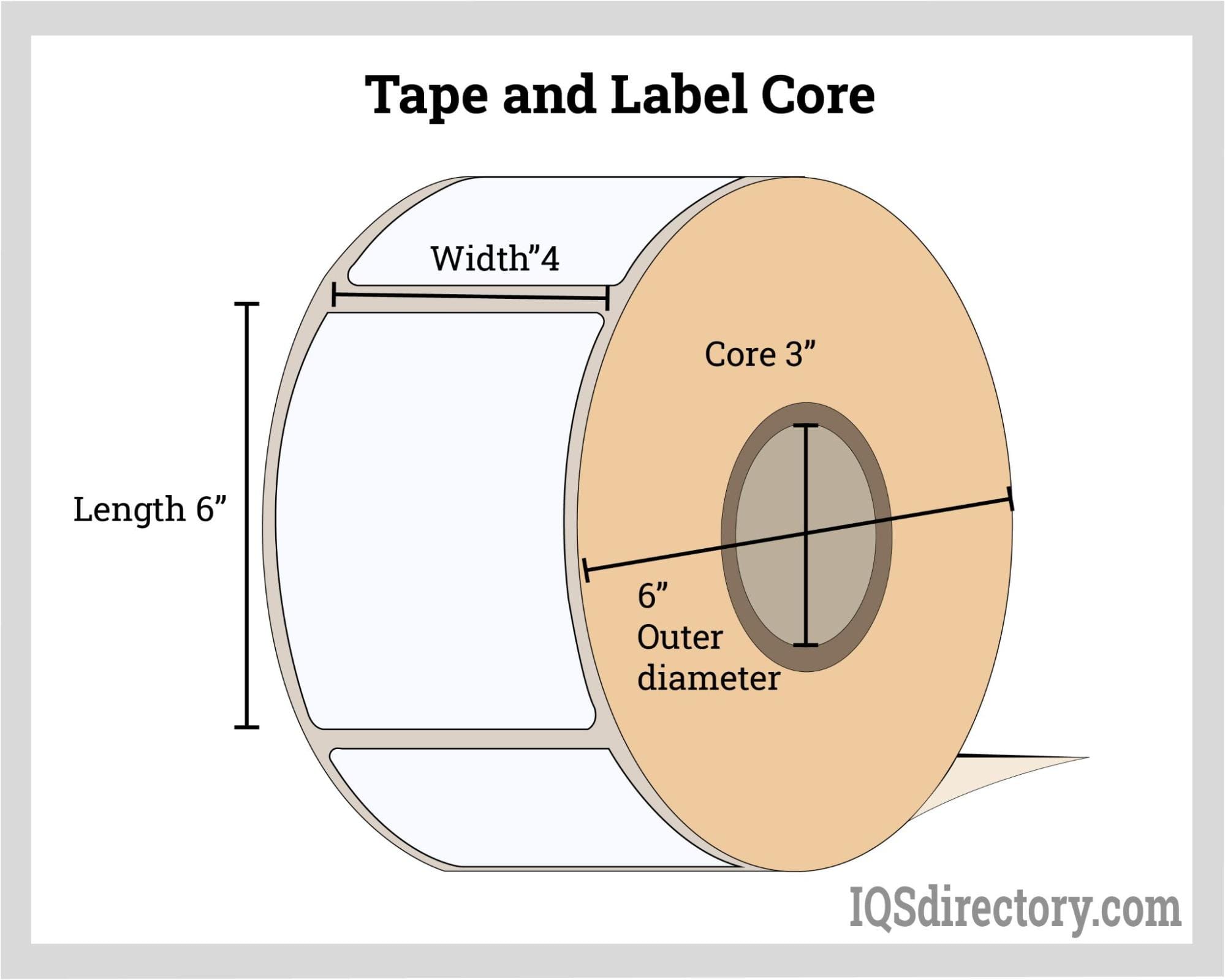
- Adhesive Tape and Label Production: Manufacturers use sturdy tube cores for rolls of adhesive tape, labels, vinyl, and other flexible products, ensuring shape retention and ease of use.
- Food and Beverage Packaging: Food-grade cardboard tubes package dry goods like chips, snacks, spices, or powdered beverages, offering tamper-evident, lightweight, and recyclable packaging solutions.
- Industrial Arts, Displays, and Retail:
- Signage, Displays, and Exhibits: Tubes are crafted into lightweight display stands, retail fixtures, or trade show booths. Their customizability allows for eye-catching, branded presentations.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Reinforced cardboard tubes are integrated into lightweight or modular furniture, offering sustainable alternatives to metal or plastic components.
- Specialized and Technical Applications:
- Pyrotechnics: Cardboard tubes form the casings for fireworks, serving as safe, combustible structures for aerial shells and rockets.
- Automotive and Machinery Manufacturing: Tubes are used as mandrels, cores, or temporary spacers in the fabrication of cylindrical parts or during assembly processes.
- Agriculture: Biodegradable tubes act as plant pots, tree shelters, or seedling protectors, providing early-stage growth support and protection against pests or weather.
The widespread adoption of cardboard tubes is driven by their customizable dimensions, structural integrity, and eco-friendliness—most are manufactured from recycled paperboard and are fully recyclable after use. Industries value their ability to be tailored for single-use or reusable applications, their potential for branding, and their contribution to reducing packaging waste.
Cardboard tubes, crafted from resilient paperboard, are a cornerstone in sectors such as packaging, shipping, construction, manufacturing, printing, arts, and agriculture. Their adaptability makes them a practical, sustainable choice for an ever-growing range of commercial and industrial applications.
How Are Cardboard Tubes Manufactured?
The manufacturing process for cardboard tubes involves advanced engineering and precision to ensure optimal performance for each intended application. The journey typically begins with selecting high-quality paperboard—often composed of recycled fibers for sustainability. This material is trimmed to the desired width and thickness and coated with industrial adhesives for superior bonding.
Spiral Winding Method
In the spiral winding process, adhesive-coated paperboard strips are tightly wound around a rotating mandrel at a continuous spiral angle. Each layer slightly overlaps the previous one, resulting in seamless, cylindrical tubes with exceptional rigidity and uniform wall thickness. Spiral wound tubes are ideal for postal mailing, document protection, product packaging, and industrial cores.
Convolute Winding Method
Alternatively, the convolute winding technique wraps paperboard strips around the mandrel in a perpendicular or helical fashion, creating layers with visible seams. Convolute tubes often have thicker walls and a textured surface, making them suitable for cores for paper towels and tissue rolls, specialty packaging, and applications requiring enhanced grip or unique surface finishes.
Modern cardboard tube manufacturers often use automated, high-speed machinery for both winding methods, enabling precise control over tube diameter, wall thickness, and length. Some facilities offer custom fabrication, printing, and specialty coating services to meet unique customer requirements.
Curious about which manufacturing method is best for your application? Ask a supplier about the differences between spiral and convolute wound tubes, and request samples to evaluate strength, finish, and cost-effectiveness for your specific needs.
Key Components of Cardboard Tubes
The robust structure of a cardboard tube arises from several key components:
- Outer Layer: Made from high-density paperboard or kraft, this layer provides durability, surface protection, and opportunities for branding, printing, or labeling.
- Inner Layer: Usually constructed from similar or heavier-grade paperboard, the inner layer adds compression strength and resists deformation under load.
- Adhesive: Industrial-grade adhesives bond the layers, ensuring the tube maintains shape and integrity during use and handling.
Depending on the intended use, tubes may include:
- Reinforcement Layers: For heavy-duty or structural applications, tubes may incorporate additional plies of paperboard, fiberglass mesh, or plastic films for increased strength.
- Specialty Coatings: Waterproof, moisture-resistant, or greaseproof coatings protect contents from environmental factors, vital for outdoor or food-grade uses.
- End Caps: Plastic or metal end plugs seal tube ends for secure shipping and storage.
Wondering how to choose the right tube composition? Consider your product’s sensitivity to moisture, required load capacity, and branding preferences. Consult with your manufacturer about layered construction and coating options.
Limitations of Cardboard Tubes
While cardboard tubes are versatile, there are some inherent limitations to consider:
- Size Constraints: Tubes are generally best for cylindrical or near-cylindrical applications; complex shapes may be difficult or costly to achieve.
- Weight Restrictions: There are limits to the load-bearing capacity, especially for very large or long tubes without reinforcement.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Standard tubes may degrade when exposed to excessive moisture, humidity, or chemicals unless specially coated.
- Temperature Vulnerability: Extreme heat or cold can affect tube strength and longevity, making them less suitable for certain industrial or outdoor uses without modification.
Certain industries, such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, or high-temperature environments, may require alternatives or specialty-engineered cardboard tubes to meet regulatory and performance standards.
Overcoming Limitations: Recent Innovations
To address these challenges, cardboard tube manufacturers have introduced several innovations:
- Advanced Engineering: Computer-aided design (CAD) and precision winding allow for complex shapes and multi-layered structures, expanding design possibilities.
- Material Enhancement: Incorporating stronger paperboard grades, recycled content, or reinforcing fibers (like fiberglass or PLA) increases tube strength and durability.
- Specialty Coatings and Laminates: Waterproof, fire-retardant, and chemical-resistant coatings extend tube usability into harsh or regulated environments.
- Biodegradable and Compostable Options: Fully compostable tubes made from plant-based adhesives and paperboard support zero-waste and sustainable packaging initiatives.
Looking for solutions to unique packaging or structural challenges? Contact a manufacturer to discuss custom reinforcements, specialty coatings, and advanced winding techniques tailored to your needs.
The Benefits of Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard tubes offer a compelling package of benefits that make them a preferred choice across industries:
- Eco-Friendly and Sustainable: Manufactured from renewable, recyclable materials, cardboard tubes support responsible sourcing and circular economy goals. Many suppliers hold FSC or ISO 14001 certifications for sustainable practices.
- Customizable and Versatile: Available in virtually any length, diameter, or wall thickness, tubes can be precisely engineered for specific applications—from delicate poster shipping to heavy-duty construction formwork.
- Cost-Effective: Lightweight construction lowers shipping costs and reduces material expenses compared to plastic, metal, or wood alternatives.
- Superior Protection: Rigid construction prevents bending, crushing, or impact damage, while end caps and coatings safeguard against environmental hazards.
- Branding Potential: Tubes can be easily printed, labeled, or wrapped for retail packaging, promotional campaigns, or branded displays.
- Thermal Insulation: Multi-layered tubes provide basic insulation for temperature-sensitive products during short-term shipment or storage.
- Regulatory Compliance: Food-grade, fire-resistant, or moisture-resistant tubes are available to meet industry-specific requirements.
These advantages make cardboard tubes suitable for a wide range of buyer intents, from eco-conscious businesses seeking sustainable packaging to manufacturers needing robust, economical cores for industrial processes.
Common and Specialized Applications for Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard tubes are integral in diverse fields, providing both everyday and specialized solutions:
- Packaging and Shipping: Securely ship posters, blueprints, textiles, and fragile goods; tubes prevent creasing and damage in transit.
- Construction: Serve as concrete formwork for columns, piers, and footings; reduce construction costs and simplify site logistics.
- Arts, Crafts, and DIY: Form the basis for creative projects, models, prototypes, children’s crafts, and even musical instruments.
- Manufacturing: Act as winding cores for paper, vinyl, textiles, labels, and tapes, improving efficiency in high-speed processing lines.
- Agriculture: Protect seedlings as plant guards or tree shelters, supporting early growth and minimizing pest damage.
- Retail and Display: Feature in point-of-sale displays, countertop stands, and innovative packaging for product launches or seasonal campaigns.
- Medical and Laboratory: Used as specimen containers, sample holders, or disposable supports in research and diagnostics.
- Specialized Industrial Uses: Custom tubes for explosives, fireworks, or machinery parts, showcasing the adaptability of advanced winding and coating technologies.
Want to explore creative uses for cardboard tubes? Browse case studies of how industries—from retail to aerospace—innovate with custom tube designs for unique challenges.
How to Select the Best Cardboard Tube for Your Application
Selecting the most appropriate cardboard tube requires an understanding of your specific needs and the available customization options. Consider these decision factors:
- Dimensions: Choose diameter, length, and wall thickness based on the size and weight of the items you need to protect, store, or ship.
- Strength and Durability: Match tube construction to the required load-bearing capacity—thicker walls and reinforced materials for heavier or high-stress applications.
- Environmental Resistance: For outdoor or humid environments, opt for tubes with waterproof or moisture-resistant coatings.
- Compliance Requirements: Food, medical, or hazardous material applications may require certified, specialty-grade tubes.
- Customization and Branding: If visual impact is important, seek tubes that support high-quality printing or custom finishes.
Trying to determine the right tube for your business? Request samples, conduct performance tests, and consult with suppliers about custom reinforcement, coatings, and eco-friendly options.
How to Choose the Best Cardboard Tube Supplier
Choosing a reliable cardboard tube manufacturer or supplier is crucial to ensure product quality, consistent supply, and optimal value. Follow this step-by-step guide:
- Define Your Requirements:
- Clarify intended use (packaging, mailing, construction, industrial cores, etc.), desired dimensions, strength, and any special features (e.g., moisture resistance, food-grade, custom printing).
- Determine your order volume and frequency—one-off bulk orders or ongoing supply contracts.
- Assess Quality and Specifications:
- Look for proven manufacturing standards, consistent material quality, and the ability to customize tube specifications for your application.
- Ask about product certifications, testing protocols, and quality assurance processes.
- Evaluate Manufacturing Capabilities:
- Ensure suppliers have sufficient production capacity, advanced machinery, and flexibility to accommodate urgent or custom orders.
- Check if they offer a variety of tube types (spiral-wound, convolute-wound, specialty shapes).
- Check Reliability and Lead Times:
- Research their delivery record, logistics capabilities, and proximity to your location for faster turnaround.
- Clarify standard and expedited lead times, especially for time-critical projects.
- Compare Pricing and Value:
- Request quotes from multiple suppliers, weighing price against quality and customization options.
- Inquire about bulk discounts, minimum order quantities, and flexible contract terms.
- Verify Sustainability Practices:
- Prioritize suppliers using recycled or certified materials, and those with recognized environmental certifications (FSC, ISO 14001).
- Ask about waste reduction and recycling programs within their operations.
- Review Customer Service and Support:
- Test responsiveness to inquiries and willingness to provide technical advice or guidance for custom projects.
- Choose suppliers with strong industry experience and a track record of proactive support.
- Check Certifications and Compliance:
- For regulated applications, confirm adherence to relevant standards (FDA for food packaging, structural codes for construction, ISO 9001 for quality management).
- Seek Reviews and References:
- Look for testimonials, case studies, or peer reviews, especially from businesses with similar requirements.
- Request references from the supplier to verify reliability and service quality.
- Test with a Small Order:
- Place a trial order to evaluate product quality, delivery accuracy, and overall service before committing to larger contracts.
Selecting the right supplier is about more than just price—consider their ability to provide tailored solutions, rapid delivery, and sustainable practices. A well-matched supplier will not only meet your current requirements but will also be a valuable partner as your business grows or diversifies.
Ready to find your ideal supplier? Use our directory of vetted cardboard tube manufacturers—featuring detailed profiles, direct contact forms, and our patented website previewer—for efficient supplier comparison. Submit a single RFQ form to reach multiple suppliers and streamline your procurement process.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cardboard Tubes
- How do I know which cardboard tube is best for my product? Consider the weight, dimensions, and sensitivity of your product. Consult suppliers for recommendations and sample testing.
- Can cardboard tubes be reused or recycled? Yes. Most tubes are recyclable and many are designed for multiple-use cycles, reducing environmental impact.
- Are custom sizes or printed designs available? Leading manufacturers offer extensive customization, including size, wall thickness, coatings, and full-color printing for branding.
- What is the lead time for custom orders? Lead times vary by complexity and order volume; always confirm with your chosen supplier.
- What certifications should I look for in a supplier? For sustainability, seek FSC or ISO 14001. For food or medical use, confirm relevant regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA).
Need more answers? Contact our featured manufacturers directly through their profile pages or submit your inquiry via our centralized RFQ form.
Explore Related Packaging Solutions
If your business requires additional packaging solutions, such as flexible bags, film wraps, or specialty containers, visit our Plastic Bags website for a comprehensive selection of high-quality, customizable products.
In summary, cardboard tubes are a foundational packaging and industrial solution, valued for their sustainability, versatility, and customizability. From protecting valuable goods in transit to serving as integral parts of construction, manufacturing, arts, and agriculture, their importance continues to grow as businesses seek eco-friendly, reliable, and cost-effective alternatives to plastic and metal. By understanding their uses, manufacturing methods, benefits, and selection criteria, you can make informed decisions that drive operational efficiency and environmental stewardship.








 Cardboard Tubes
Cardboard Tubes Carrying Cases
Carrying Cases Contract Packaging
Contract Packaging Corrugated Boxes
Corrugated Boxes Dot Peening Machines
Dot Peening Machines Labeling Machinery
Labeling Machinery Marking Machinery
Marking Machinery Packaging Equipment
Packaging Equipment Palletizers
Palletizers Plastic Bags
Plastic Bags Sewing Contractors
Sewing Contractors Tape Suppliers
Tape Suppliers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services